Cloud Computing: A Beginner's Guide to the Cloud
January 15, 2025

Picture a scenario where companies no longer depend on large, cumbersome servers. Also, high-cost IT setups are no longer required to run their daily processes. Instead, they turn to cloud computing architecture—a groundbreaking methodology transforming how organisations save, access, as well as, process data.
A recent Gartner study reveals that global expenditure on cloud computing technology will reach $700 billion in 2025 as hybrid work culture spreads.
Whether you are experienced or just starting in this domain, this guide will navigate you through everything you need to understand about the revolutionary cloud computing technology. Let us begin with the cloud computing definition.
What is Cloud Computing?
To understand the basic concepts of cloud computing, consider it as leasing rather than owning. Traditionally, organisations acquired physical servers to handle their applications and store data. However, cloud computing technology removes the necessity for on-site infrastructure. It does so by enabling users to access computing resources. This involves software, servers, and storage via the internet, as needed.
The cloud computing definition can be encapsulated as a service delivery model for IT resources. It lets users access and utilise resources through the internet. Rather than buying and maintaining hardware, users depend on external providers to oversee resources while only paying for what they consume.
A straightforward analogy? It is akin to drawing electricity from a grid instead of operating a generator at home. This ease of access is the reason why organisations of every magnitude are embracing cloud architecture in cloud computing to maintain a competitive edge.
Different Types of Cloud Computing
Knowing the distinct cloud computing types is key. This understanding is crucial for identifying the ideal solution for your requirements. The three main categories include:
- Public Cloud
- Operated by third-party providers. This involves Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform.
- Ideal for organisations seeking cost efficiency and scalability.
- Accessible to multiple customers via the Internet.
- Private Cloud
- Exclusively used by a single organisation.
- Offers enhanced control, security, and privacy.
- Usually installed on-premises or handled by an outside service provider.
- Hybrid Cloud
- Combines public and private clouds.
- Allows businesses to balance scalability with security.
- Perfect for organisations needing flexibility for sensitive and non-sensitive operations.
Each type has its advantages and shortcomings. Therefore, understanding your organisation's requirements is key to leveraging the right cloud architecture in cloud computing.
Types of Cloud Computing Service Models
The adaptability of cloud computing architecture resides in its service models. These models address various business requirements. The primary types of cloud computing models include:
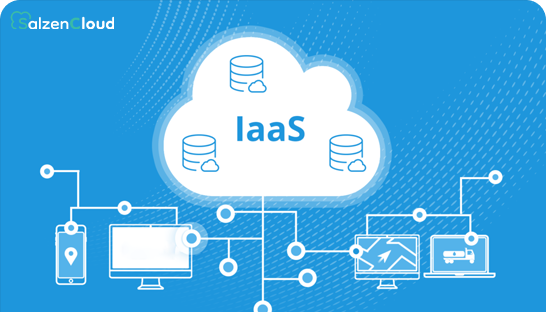
- Infrastructure as a Service
- Provides virtualised computing resources like networking, servers, and storage.
- Users manage applications, data, and operating systems while the provider handles the infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service
- Puts forward a development platform for building and deploying applications.
- Removes the need to manage operating systems and hardware.
- Software as a Service
- Provides software applications via the internet on a subscription model.
- Illustrative examples include Microsoft 365 and Salesforce.
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses

The embrace of cloud computing technology goes beyond being a simple trend. It has evolved into a deliberate, strategic choice for organisations striving to excel today. Companies are no longer viewing technology merely as a tool. Instead, they see it as a means to innovate, curb expenses, and unlock extraordinary growth possibilities.
Let us examine three thorough advantages of cloud architecture in cloud computing and how they are influencing the future of enterprises.
- Cost Efficiency
One of the most immediate and quantifiable advantages of cloud computing architecture is the considerable decrease in IT expenses. Organisations no longer need to invest in costly physical servers, data centres, or IT infrastructure. Maintenance costs, which frequently consume a significant portion of IT budgets, are substantially lowered as cloud providers take care of all infrastructure management. This encompasses hardware upgrades and software updates.
The pay-as-you-go model guarantees optimal resource utilisation. For example, a startup requiring minimal computing power pays solely for what they consume. In contrast, a large enterprise can scale its operations efficiently without acquiring additional hardware. This transition from capital expenditure to operational expenditure is especially advantageous for organisations with constrained budgets or varying demands.
- Scalability and Flexibility
The capability to scale effortlessly is one of the hallmark characteristics of cloud architecture in cloud computing. Unlike traditional systems that demand time, financial resources, and effort to increase capacity, the cloud enables organisations to modify resources instantly according to current requirements.
An eCommerce platform, for instance, experiencing a spike in traffic during a holiday sale can promptly scale up server capacity to manage the heightened demand. Likewise, resources can be scaled down to prevent unnecessary expenditures after the event concludes. This flexibility ensures that organisations are always prepared to meet customer demands without incurring additional costs or delays.
Furthermore, this scalability has a global reach. Deploying applications and services across various regions is seamless for firms, needing a few taps. This connects them with customers worldwide without the need to establish a physical infrastructure.
- Robust Security and Disaster Recovery
One prevalent concern regarding cloud computing technology is data security. However, contemporary cloud computing architecture frequently exceeds the security benchmarks of traditional on-premises systems. Leading cloud providers invest significantly in sophisticated security measures, including:
- Encryption: Safeguards sensitive information during transmission and while stored. This renders it unreachable to unauthorised individuals.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Introduces an additional security layer by necessitating multiple verification forms to access systems.
- Regular Updates: Guarantees that systems are shielded against emerging cyber threats.
Furthermore, cloud computing technology streamlines disaster recovery. This is a vital aspect that organisations often neglect. With traditional configurations, data recovery following a system failure or natural calamity can require days or weeks. In contrast, cloud-powered systems provide automated backups and failover mechanisms that ensure minimal downtime. Organisations can swiftly resume operations. This helps mitigate potential revenue loss and preserve customer confidence.
The Bottom Line
Cloud computing has transformed how organisations function by putting forward outstanding scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. For newcomers entering the cloud computing realm, grasping the different deployment and service models is essential for making well-informed choices. We hope this blog has clarified what is cloud computing and the very ins and outs of it in detail.
Whether you are a small startup or a large corporation, the cloud presents solutions customised to your specific requirements and growth path. So, what are you holding for? Channelise the strength of cloud computing to have a foot forward in the race!
For more information on cloud computing technology, monitoring, and cost optimisation, visit the Salzen Cloud website.
recent blogs

10 Ways to Choose the Right Infrastructure as a Service Provider
Read More